Managing blackouts using the event API
Two main ways of communication can be used to send events to the cell and manage blackouts. Depending on architecture or security impacts one or both methods can be used.
Here is a summary for each solution:
|
Solution |
Communication details |
Benefits |
Drawbacks |
|
Msend |
From host to BMC Impact manager over TCP |
Can be buffered on Windows / AIX/HP-UX and RedHat Linux Exist on all plateforms using msend.pl |
Needs connectivity to cell target (host / port / key) |
|
Rest API |
Using the TrueSight Web services REST API |
Can be integrated in other developments |
|
Using msend utility
The msend utility can be used to send events in order to manage blackout periods.
The generic syntax of the msend command line is as follows. Please see further paragraphs to use it ins specific contexts.
msend –q –n <remote cell name> -a <ClassName> –b “SlotX=ValueX;SlotY=ValueY”
Using the rest API
Events can be sent to TrueSight using the REST API of TrueSight. Please consult the BMC documentation for more details, for example :
https://communities.bmc.com/docs/DOC-44797
Create Objects blackouts using events
Using msend utility
Definition
In order to create a blackout period using the msend command line with several arguments:
The classname to create periods is SET_MAINTENANCE
Available slotnames are:
|
Slot name |
Description |
|
Host |
Host to set in blackout mode |
|
Maintenance_application_class |
Application Class to set in blackout mode. Restriction: Can be as exact as possible, support regular expressions. Default=.* (all) |
|
Maintenance_instance |
Instance to set in blackout mode. Restriction: Can be as exact as possible, support regular expressions. Default=.* (all) |
|
Maintenance_parameter |
Parameter to set in blackout mode Restriction: Can be as exact as possible, support regular expressions. Default=.* (all) |
|
MaintStart |
Start timestamp Integer value: the number of seconds since 00:00:00 UTC on January 1, 1970 (epoch time) |
|
MaintStop |
Stop timestamp Integer value: the number of seconds since 00:00:00 UTC on January 1, 1970 (epoch time) |
|
Action |
Type of BLACKOUT. Must be one of: CLOS, BLACKOUT, REOPEN |
|
ApplyToNonClosedEvents |
Define if this period apply on events existing before period start Default: NO. Must be one of: NO, SinceBlackoutCreation, EveryExistingEvents |
|
Proprietaire |
Period owner |
|
Commentaire |
Comment on this blackout period |
Sample
Using the msend command line with arguments (shell script)
NowTS=$(date +%s)
StartTS=$(($NowTS + 10))
StopTS=$(($StartTS + 120))
msend -q -n CellName -a SET_MAINTENANCE -b "Host=mysserver2; Maintenance_application_class=.*; Maintenance_instance=.*;Maintenance_parameter=.*;MaintStart=$StartTS;MaintStop=$StopTS;Action=REOPEN;Proprietaire=Robot;Commentaire='This server will reboot in few seconds'"
This will create the following blackout periods: Starting 10 seconds from now and with with a 120 seconds duration.

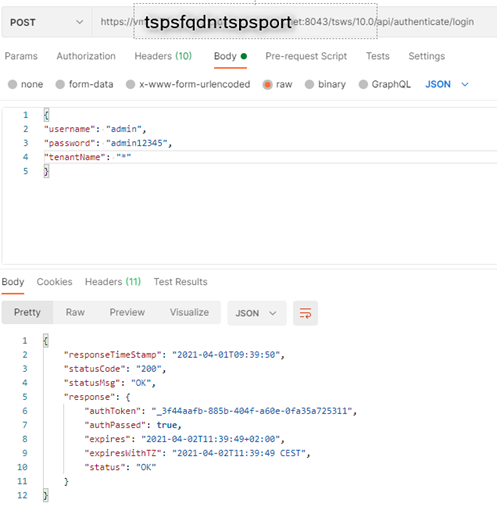
Using the REST API:
Authentication
Send event
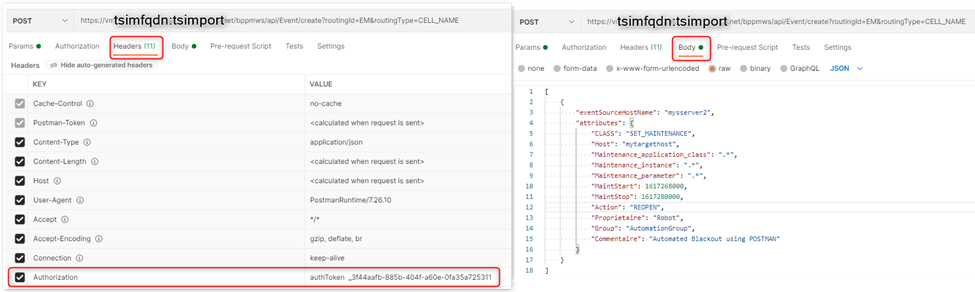
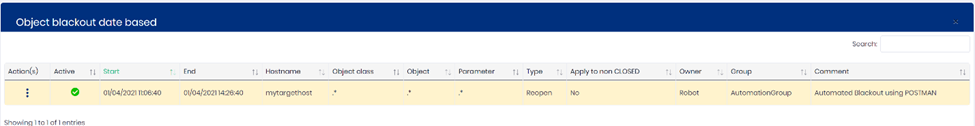
Will create
Delete Objects blackouts using msend
This section is describing how to delete existing periods but have no impact on existing events.
Definition
In order to delete a blackout period using the msend command line with several arguments:
The classname to destroy existing periods is UNSET_MAINTENANCE.
The following slots must be equal to the creation ones:
|
Slot name |
Description |
|
Host |
Host to set in blackout mode Restriction: Should be as exact as possible |
|
Maintenance_application_class |
Application Class to set in blackout mode. Restriction: Can be as exact as possible, support regular expressions. Default=.* (all) |
|
Maintenance_instance |
Instance to set in blackout mode. Restriction: Can be as exact as possible, support regular expressions. Default=.* (all) |
|
Maintenance_parameter |
Parameter to set in blackout mode Restriction: Can be as exact as possible, support regular expressions. Default=.* (all) |
|
MaintStart |
Start timestamp Integer value: the number of seconds since 00:00:00 UTC on January 1, 1970 |
|
MaintStop |
Stop timestamp Integer value: the number of seconds since 00:00:00 UTC on January 1, 1970 |
Sample
Using the msend command line with arguments :
NowTS=$(date +%s)
StartTS=$(($NowTS + 10))
StopTS=$(($StartTS + 120))
msend -q -n CellName -a SET_MAINTENANCE -b "Host=mysserver2; Maintenance_application_class=.*; Maintenance_instance=.*;Maintenance_parameter=.*;MaintStart=$StartTS;MaintStop=$StopTS;Action=REOPEN;Proprietaire=Robot;Commentaire='This server will reboot in few seconds'"
read
msend -q -n CellName -a UNSET_MAINTENANCE -b "Host=mysserver2; Maintenance_application_class=.*; Maintenance_instance=.*;Maintenance_parameter=.*;MaintStart=$StartTS;MaintStop=$StopTS"Will delete previoulsy created blackout periods
Stop running Object blackout using msend
This section is describing how to stop existing periods, this will have impact on existing events but will not delete periods.
Definition
In order to stop a blackout period using the msend command line with several arguments:
The classname to delete existing periods is STOP_MAINTENANCE.
The following slots must be equal to the creation ones:
|
Slot name |
Description |
|
Host |
Host to set in blackout mode |
|
Maintenance_application_class |
Application Class to set in blackout mode. Restriction: Can be as exact as possible, support regular expressions. Default=.* (all) |
|
Maintenance_instance |
Instance to set in blackout mode. Restriction: Can be as exact as possible, support regular expressions. Default=.* (all) |
|
Maintenance_parameter |
Parameter to set in blackout mode Restriction: Can be as exact as possible, support regular expressions. Default=.* (all) |
|
MaintStopDelay |
Duration (en seconds) from event to real period removal. |
Sample
Using the msend command line with arguments :
NowTS=$(date +%s)
StartTS=$(($NowTS + 10))
StopTS=$(($StartTS + 120))
msend -q -n CellName -a SET_MAINTENANCE -b "Host=mysserver2; Maintenance_application_class=.*; Maintenance_instance=.*;Maintenance_parameter=.*;MaintStart=$StartTS;MaintStop=$StopTS;Action=REOPEN;Proprietaire=Robot;Commentaire='This server will reboot in few seconds'"
msend -q -n CellName -a STOP_MAINTENANCE -b "Host=mysserver2; Maintenance_application_class=.*; Maintenance_instance=.*;Maintenance_parameter=.*;MaintStart=$StartTS;MaintStop=$StopTS;Action=REOPEN;Proprietaire=Robot;Commentaire='This server will reboot in few seconds'"
Will create blackout periods:

msend -q -n CellName -a STOP_MAINTENANCE -b "Host=mysserver2; Maintenance_application_class=.*; Maintenance_instance=.*;Maintenance_parameter=.*;MaintStart=$StartTS;MaintStop=$StopTS;Action=REOPEN;Proprietaire=Robot;Commentaire='This server will reboot in few seconds'"
Will stop the blackout .
Stop and delete running periods using msend
This section is describing how to stop existing periods, this will have impact on existing events and will delete periods.
This can only be used on Object / Date periods.
Definition
In order to stop a blackout period using the msend command line with several arguments:
The classname to delete existing periods is STOPANDDDESTROY_MAINTENANCE.
The following slots must be equal to the creation ones:
|
Slot name |
Description |
|
Host |
Host to set in blackout mode Restriction: Should be as exact as possible |
|
Maintenance_application_class |
Application Class to set in blackout mode. Restriction: Can be as exact as possible, support regular expressions. Default=.* (all) |
|
Maintenance_instance |
Instance to set in blackout mode. Restriction: Can be as exact as possible, support regular expressions. Default=.* (all) |
|
Maintenance_parameter |
Parameter to set in blackout mode Restriction: Can be as exact as possible, support regular expressions. Default=.* (all) |
|
MaintStart |
Start timestamp Integer value: the number of seconds since 00:00:00 UTC on January 1, 1970 |
|
MaintStop |
Stop timestamp Integer value: the number of seconds since 00:00:00 UTC on January 1, 1970 |
Sample
Using the msend command line with arguments :
msend -q -n CellName -a STOPANDDESTROY_MAINTENANCE -b "Host=mysserver2; Maintenance_application_class=.*; Maintenance_instance=.*;Maintenance_parameter=.*;MaintStart=$StartTS;MaintStop=$StopTS;Action=REOPEN;Proprietaire=Robot;Commentaire='This server will reboot in few seconds'"Will stop and delete previously created blackout period:

It will impact events and remove period definition.
Create Custom Blackouts
Definition
Custom blackouts (see chapter) can be created using events. The content of such events must be inline with the definition of an existing custom blackout definition.
Using events to manage custom blackouts requires to load the files CustomMaintenance_Event.baroc and CustomMaintenance_Event.mrl KB files (see chapter )
The classname to create periods is SET_CUSTOM_MAINTENANCE.
Slot values to provide in the event are as follows.
|
Slot name |
Description |
|
CustomBlackoutName |
Name of the custom blackout type. This name must correspond to one of the custom blackout types as stored in the file CustomPeriods.cfg (see chapter) |
|
SelectorSlotsList |
List of the event slots that are used to build the slot conditions in the custom blackout. |
|
SelectorOperatorsList |
List of the test operators used to build the slot conditions. The number of elements in the list must match the number of slots listed in the SelectorSlotsList Supported operators are : "has_prefix", "has_suffix", "ip_match", "contains", "match_regex", "equals", "not_equals", "greater_or_equals", "smaller_or_equals", "greater_than", "smaller_than" |
|
SelectorValuesList |
List of the values used to build the slot conditions. The number of elements in the list must match the number of slots listed in the SelectorSlotsList |
|
IsaCalendar |
Flag. Default is NO. - If set to YES, the blackout will be of type “calendar”, using the TIME_FRAME object provided in the slot CalendarName - If set to NO, the blackout will be of type “date based”, using the MaintStart and MaintStop slot values. |
|
MaintStart |
Start timestamp. Considered only if IsaCalendar=NO Integer value: the number of seconds since 00:00:00 UTC on January 1, 1970 (epoch time). Will be set to the current time if empty. |
|
MaintStop |
Stop timestamp. Considered only if IsaCalendar=NO Integer value: the number of seconds since 00:00:00 UTC on January 1, 1970 (epoch time) |
|
CalendarName |
Name of TIME_FRAME to use. Considered only if IsaCalendar=YES |
|
Action |
Type of BLACKOUT. Default is REOPEN Must be one of: CLOS, BLACKOUT, REOPEN |
|
Proprietaire |
Optional - Period owner (user) |
|
Group |
Optional - Period owner (group) |
|
Commentaire |
Optional - Comment on this blackout period |
- The event API only supports slots (as set in SelectorSlotsList) of type STRING or ENUM
- The event API does not support the “within” and “outside” test operators
- The API cannot verify is the provided values (CustomBlackoutName, SelectorSlotsList, SelectorOperatorsList) are inline with the definition of an existing custom blackout.
Sample
The following sample uses the custom blackout definition provided in Custom blackout full sample
msend -q -n CellName –
SET_CUSTOM_MAINTENANCE;
CustomBlackoutName=FullCapabilities;
SelectorSlotsList=['mc_host_class','mc_host,'mc_object_class','mc_object','location’];
SelectorOperatorsList=[‘equals’,’has_prefix’,’contains’,’equals',’equals’];
SelectorValuesList=[‘windows’,'vm-','NT_LOGICAL_DISKS','C:',’Houston’];
MaintStart=1530018301;
MaintStop=1530028301;
Proprietaire=ppx;
Commentaire=”CLI custom blackout”;
END
Delete Custom Blackouts
Use the class UNSET_CUSTOM_MAINTENANCE with the same following slot values as for SET_CUSTOM_MAINTENANCE :
- CustomBlackoutName
- SelectorsSlotsList
- SelectorOperatorsList
- SelectorValuesList
- IsaCalendar
- CalendarName
- MaintStart
- MaintStop
